The vitamin B complex represents a powerful group of eight essential nutrients that collectively play vital roles in maintaining optimal health and wellbeing. Unlike many vitamins that work independently, these water-soluble compounds function synergistically, supporting countless biochemical reactions throughout your body. From cellular energy production to cognitive function, the B vitamins are truly fundamental to human health.
Often described as the body’s “power house” vitamins, the B complex includes thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridoxine (B6), biotin (B7), folate (B9), and cobalamin (B12). Each member has distinct functions, yet they collaborate closely to ensure proper metabolic functioning, neurological health, and cellular maintenance.
Understanding the comprehensive benefits of these micronutrients can help you make informed decisions about your nutritional intake and supplement regimen. Let’s explore the ten essential ways vitamin B complex supports your health and why ensuring adequate levels should be a priority in your wellness routine.

1. Boosts Energy Production
At a cellular level, B vitamins are critical components in the intricate process of converting food into usable energy. This transformation isn’t just important—it’s the fundamental biochemical process that powers every function in your body.
Thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), and niacin (B3) play particularly significant roles in this energy production cycle. These vitamins function as essential coenzymes in the metabolic pathways that convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into adenosine triphosphate (ATP)—the molecule that serves as your body’s primary energy currency.
When B vitamin levels are optimal, your cellular metabolism operates efficiently, helping to combat fatigue and enhance overall vitality. Many people report noticeable improvements in their energy levels after addressing B vitamin deficiencies. This energy-boosting effect is why B vitamins are often included in supplements marketed for increased stamina and reduced fatigue.
Research has demonstrated that B vitamins are particularly crucial for individuals with high-energy demands, including athletes, physically active individuals, and those recovering from illness or surgery. The energy conversion process supported by B vitamins doesn’t produce a stimulant effect like caffeine; rather, it optimizes your body’s natural energy production systems at the cellular level.
2. Supports Brain Health and Cognitive Function
The relationship between B vitamins and neurological health is profound and multifaceted. These nutrients are integral to both the structural integrity of your brain and its functional capabilities.
B vitamins, particularly B1, B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are essential for neurotransmitter synthesis—the chemical messengers that enable communication between brain cells. These neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, regulate mood, motivation, cognition, and numerous other brain functions.
Additionally, several B vitamins contribute to the formation and maintenance of myelin sheaths—the protective coating around nerve fibers that ensures proper signal transmission. B12 is especially critical in this regard, with deficiencies potentially leading to demyelination and subsequent neurological complications.
Research consistently demonstrates that adequate B vitamin levels support memory, concentration, and overall cognitive performance. Long-term studies have linked B vitamin deficiencies to increased risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative conditions. In fact, a landmark Oxford University study found that supplementing with B6, B9, and B12 could slow brain atrophy in elderly people with mild cognitive impairment.
For professionals with high cognitive demands, students, and older adults concerned about maintaining mental sharpness, ensuring optimal B vitamin status may provide significant neurological benefits and protection.
3. Promotes Healthy Skin, Hair, and Nails
B vitamins play crucial roles in maintaining the health and appearance of your skin, hair, and nails—often serving as nature’s beauty supplements. These nutrients support the development and maintenance of these tissues at the cellular level.
The connection between B vitamins and appearance is most evident in their role in cell regeneration and division. Skin cells, in particular, have one of the highest turnover rates in the body, and B vitamins are essential for supporting this continuous renewal process. Riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), and folate (B9) are particularly important for skin cell regeneration and repair.
Biotin (B7) has earned its reputation as the “beauty vitamin” due to its fundamental role in maintaining the structure of keratin—the primary protein in hair and nails. Clinical studies have shown that biotin supplementation can improve hair strength and thickness while reducing brittleness in nails.
B vitamins also play significant roles in managing skin conditions. Niacin (B3) helps maintain skin barrier function and has been shown to improve conditions like acne and rosacea. Pantothenic acid (B5) has demonstrated effectiveness in reducing oil production and improving acne.
Deficiencies in B vitamins often manifest visibly through skin concerns, including dermatitis, cracks at the corners of the mouth, pale or easily bruised skin, or premature aging. Hair may become brittle or dull, and nails may become ridged or split easily.
4. Enhances Mood and Mental Wellbeing
The relationship between B vitamins and mental health represents one of the most promising areas of nutritional psychiatry research. These nutrients directly influence your brain’s production and regulation of mood-related neurotransmitters.
B vitamins, particularly B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are essential cofactors in synthesizing and regulating neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA—the chemical messengers responsible for feelings of wellbeing, motivation, and calm. Without adequate B vitamins, these neurotransmitter systems can become dysregulated, potentially contributing to mood disorders.
Research has established significant connections between B vitamin status and mental health. Multiple studies have found that individuals with depression often have lower levels of folate and B12. In fact, some research indicates that patients with depression who have low folate levels may respond less effectively to antidepressant medications.
B vitamins also play important roles in managing stress responses. Pantothenic acid (B5) supports adrenal function, while B6 facilitates the body’s production of calming neurotransmitters. During periods of high stress, B vitamin requirements may increase, making supplementation particularly beneficial during challenging life phases.
The mood-stabilizing effects of B vitamins appear to be most pronounced in individuals with pre-existing deficiencies, but emerging research suggests benefits may extend to the general population as well, particularly as preventative support for mental wellbeing.
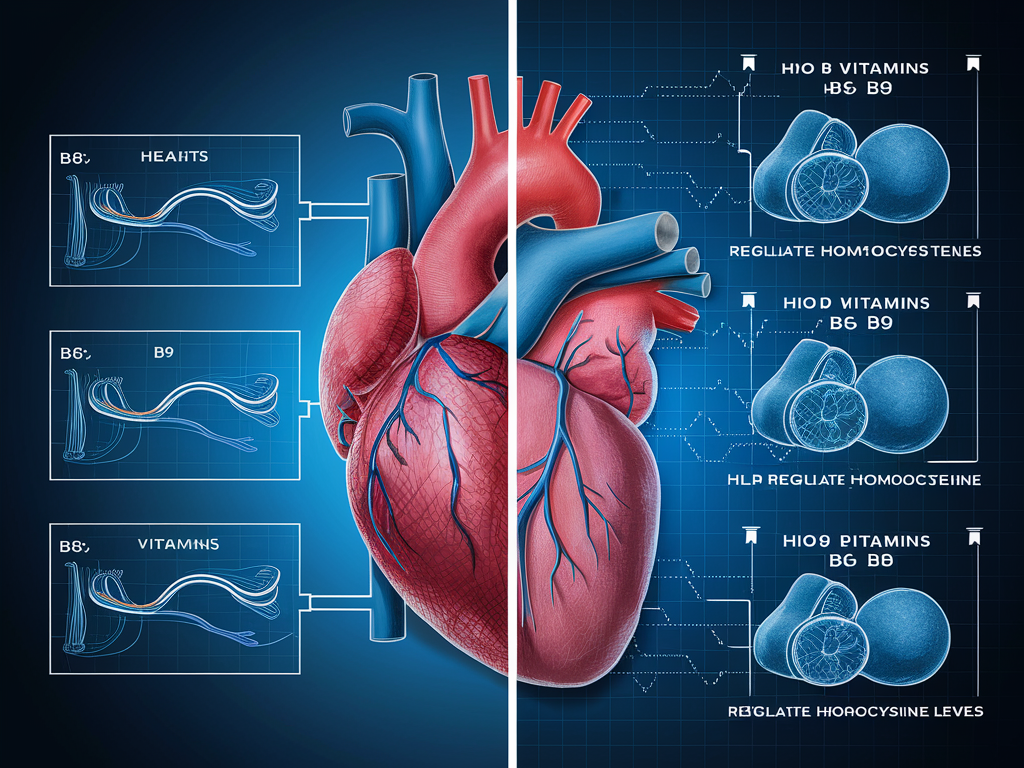
5. Supports Cardiovascular Health
The vitamin B complex provides multifaceted support for your cardiovascular system, influencing several pathways that affect heart health and circulatory function.
One of the most significant cardiovascular benefits of B vitamins relates to homocysteine management. Homocysteine is an amino acid that, when elevated, serves as an independent risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and blood vessel damage. B6, folate (B9), and B12 work together in a metabolic process that converts homocysteine to safer compounds. Research consistently shows that proper B vitamin status helps maintain healthy homocysteine levels, potentially reducing cardiovascular risk.
Beyond homocysteine regulation, niacin (B3) has been used therapeutically for decades to improve cholesterol profiles. At higher doses (under medical supervision), niacin can increase HDL (good) cholesterol while lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides. This lipid-modifying effect makes niacin a valuable tool in comprehensive heart health strategies.
B vitamins also support healthy blood pressure regulation. Riboflavin (B2) has been shown in clinical trials to reduce blood pressure in certain genetically susceptible individuals, while folate improves endothelial function—the ability of blood vessels to dilate and contract properly.
The cardiovascular benefits of B vitamins appear most pronounced in individuals with existing deficiencies or specific genetic variations affecting B vitamin metabolism. However, maintaining optimal B vitamin status is considered a prudent strategy for overall heart health maintenance for most adults.
6. Improves Digestive Health
The digestive benefits of B vitamins are among their least discussed but most fundamental functions. These nutrients play essential roles in supporting the complex processes of digestion, absorption, and gut health maintenance.
B vitamins are crucial for the production and function of digestive enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Without these enzymes, proper nutrient absorption becomes compromised, potentially leading to nutritional deficiencies despite adequate intake.
Several B vitamins, including niacin (B3) and pantothenic acid (B5), support the integrity and function of the digestive tract lining. This epithelial barrier is crucial not only for nutrient absorption but also for preventing inappropriate substances from entering the bloodstream—a condition often referred to as “leaky gut.”
B vitamins also support the energy needs of rapidly dividing intestinal cells. The digestive tract undergoes continuous cellular renewal, and B vitamins provide the metabolic support necessary for this energy-intensive process.
Research suggests that B vitamin status may influence gut microbiome composition and diversity. The gut microbiome—the complex community of bacteria living in your digestive tract—plays crucial roles in digestion, immunity, and even mood regulation. Some B vitamins serve as essential nutrients for beneficial gut bacteria, helping maintain a healthy bacterial balance.
For individuals with digestive concerns, ensuring optimal B vitamin status may help improve overall digestive comfort, nutrient absorption efficiency, and gut function.
7. Strengthens Immune System Function
B vitamins serve as critical foundational nutrients for immune system function, supporting multiple aspects of your body’s defense mechanisms against pathogens and disease.
These essential nutrients contribute significantly to immune cell production and proliferation. B vitamins, particularly folate (B9) and B12, are necessary for DNA synthesis and cellular division—processes fundamental to producing the white blood cells that identify and neutralize threats to your health.
Beyond supporting immune cell production, B vitamins are essential for antibody synthesis. Antibodies are specialized proteins that recognize and help eliminate specific pathogens. Without adequate B vitamins, antibody production may be compromised, potentially reducing your immune system’s ability to recognize and remember specific threats.
B vitamins also play important roles in regulating inflammation—a critical component of immune function. Vitamin B6, in particular, helps modulate inflammatory responses, ensuring they’re strong enough to address threats without becoming excessive and damaging to healthy tissues.
Research has demonstrated that deficiencies in various B vitamins can impair multiple aspects of immune function. Conversely, correcting these deficiencies typically restores normal immune responses. This relationship is particularly important for populations at higher risk for B vitamin deficiencies, including older adults, individuals with certain gastrointestinal conditions, and those following restrictive diets.
The immune-supporting effects of B vitamins aren’t about boosting immunity beyond normal levels but rather ensuring your immune system has the nutritional foundation to function optimally and respond appropriately to challenges.
8. Supports Healthy Pregnancy and Fetal Development
The importance of B vitamins during pregnancy cannot be overstated, as these nutrients play critical roles in supporting both maternal health and proper fetal development.
Folate (B9) stands out as perhaps the single most crucial prenatal nutrient. Adequate folate levels before conception and during early pregnancy dramatically reduce the risk of neural tube defects—serious birth abnormalities affecting the brain, spine, or spinal cord. This protective effect is so significant that many countries mandate folate fortification of grain products, and prenatal supplementation with folic acid (the synthetic form of folate) is standard medical advice.
Beyond neural tube formation, folate supports overall fetal growth and development. It’s essential for DNA synthesis and cellular division—processes that occur rapidly during fetal development.
Vitamin B12 works closely with folate and is equally important during pregnancy. B12 deficiency during pregnancy has been associated with increased risks of preterm birth, low birth weight, and neural tube defects. Additionally, maternal B12 status affects the B12 reserves a newborn will have for the first several months of life.
Other B vitamins support maternal health during the increased physiological demands of pregnancy. B6 helps manage morning sickness and supports the significant increase in protein metabolism during pregnancy. Thiamine (B1) requirements increase substantially during pregnancy to support the mother’s elevated energy needs and the development of the fetal brain.
Research consistently demonstrates that adequate B vitamin status before and during pregnancy not only reduces birth defect risks but may also support optimal cognitive development and reduce pregnancy complications.
9. Helps Maintain Healthy Red Blood Cells
Several B vitamins play irreplaceable roles in red blood cell formation, function, and maintenance—making them crucial nutrients for energy levels, oxygen transport, and overall vitality.
Vitamin B12 and folate (B9) are particularly essential for erythropoiesis—the process of red blood cell formation. These vitamins support the development of red blood cells in the bone marrow and ensure they mature properly with the correct size and function. Without adequate B12 and folate, red blood cells may develop abnormally, becoming larger than normal (megaloblastic) and less efficient at carrying oxygen.
This connection to red blood cell health explains why fatigue is often the first symptom of B12 or folate deficiency. When red blood cells cannot efficiently carry oxygen throughout the body, energy production at the cellular level becomes compromised, leading to persistent tiredness, weakness, and reduced exercise capacity.
Vitamin B6 also contributes to red blood cell metabolism by helping form hemoglobin—the iron-containing protein in red blood cells responsible for oxygen transport. Without sufficient B6, hemoglobin synthesis can be impaired.
Riboflavin (B2) protects red blood cells from oxidative damage and supports iron metabolism—another crucial component of red blood cell function.
The blood-related benefits of B vitamins are so significant that B12 injections were once common treatments for fatigue and various health complaints. While such indiscriminate use has decreased, medical professionals still recognize the profound impact B vitamin status has on red blood cell health and subsequent energy levels.
For individuals with unexplained fatigue, particularly when accompanied by pale skin, shortness of breath, or dizziness, evaluating B vitamin status—especially B12 and folate—may identify a treatable nutritional cause.

10. Supports Healthy Aging and Longevity
As research on healthy aging advances, B vitamins have emerged as key nutrients supporting cellular health and function throughout the lifespan. Their role in maintaining vitality during aging occurs through multiple biological pathways.
B vitamins, particularly folate and B12, are essential for DNA repair and maintenance—processes that become increasingly important with age. As we grow older, DNA damage accumulates naturally, but proper B vitamin status helps support the body’s repair mechanisms, potentially slowing certain aspects of the aging process at the cellular level.
Cognitive protection represents another significant anti-aging benefit of B vitamins. Long-term research has associated adequate B vitamin status—especially B6, folate, and B12—with reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline and dementia. These neuroprotective effects appear to work through multiple mechanisms, including homocysteine reduction, support for neurotransmitter production, and maintenance of myelin integrity in the brain.
B vitamins also support energy metabolism throughout aging. Many older adults experience declining energy levels partly due to less efficient cellular energy production. B vitamins help maintain metabolic efficiency, potentially supporting greater vitality and functional capacity with advancing age.
Research on centenarians—individuals who live past 100 years—has frequently identified optimal B vitamin status as a common characteristic. While no single nutrient determines longevity, the fundamental cellular functions supported by B vitamins appear increasingly important as we age.
For adults concerned about healthy aging, maintaining optimal B vitamin status through diet and, when necessary, supplementation represents a scientifically supported strategy for supporting cellular health, cognitive function, and overall vitality throughout the lifespan.
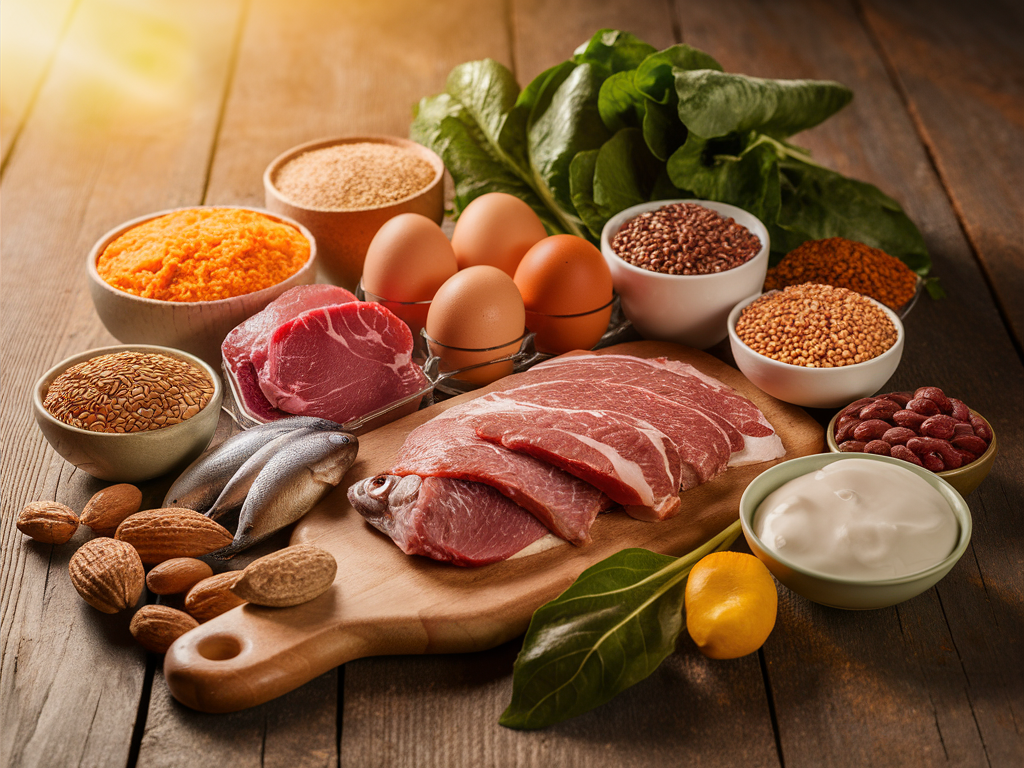
Food Sources of B Vitamins
Obtaining B vitamins through whole foods provides these nutrients in their most bioavailable forms, along with complementary nutrients that support their absorption and function. A varied diet typically provides adequate amounts of most B vitamins for healthy individuals.
Animal-based foods represent some of the richest sources of B vitamins, particularly B12, which occurs naturally only in animal products. Excellent animal sources include:
- Meat: Especially organ meats like liver, as well as beef, pork, and poultry
- Seafood: Particularly salmon, trout, tuna, clams, and mussels
- Eggs: The yolks contain most of the B vitamins
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese offer riboflavin (B2) and B12
Plant-based sources can provide substantial amounts of many B vitamins, though B12 remains a concern for those following strictly plant-based diets. Excellent plant sources include:
- Whole grains: Brown rice, barley, and products made with whole wheat
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and various beans are excellent sources of many B vitamins
- Nuts and seeds: Sunflower seeds, almonds, and other nuts provide several B vitamins
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens offer folate and other B vitamins
- Nutritional yeast: Often fortified with B12, making it valuable for plant-based diets
- Fortified foods: Many plant-based milks, breakfast cereals, and meat alternatives are fortified with B vitamins
For specific B vitamins, these foods are particularly noteworthy:
- Thiamine (B1): Whole grains, pork, beans, nuts
- Riboflavin (B2): Dairy products, eggs, green vegetables
- Niacin (B3): Meat, fish, nuts, legumes, grains
- Pantothenic Acid (B5): Widely distributed in both animal and plant foods
- Vitamin B6: Poultry, fish, potatoes, bananas, chickpeas
- Biotin (B7): Eggs, nuts, seeds, sweet potatoes
- Folate (B9): Leafy greens, legumes, fruits, fortified grains
- Vitamin B12: Animal products exclusively (unless fortified)
Vegetarians can typically obtain adequate B vitamins through careful food selection, though B12 may require attention through consumption of dairy and eggs. Vegans face greater challenges with B12 and should consider fortified foods or supplements to prevent deficiency.
Food processing and cooking methods can reduce B vitamin content, as these water-soluble vitamins can leach into cooking water or degrade with heat. Steaming vegetables, reducing cooking times, and consuming some foods raw can help preserve their B vitamin content.
Supplementation Guidelines
While obtaining B vitamins from whole foods is ideal, supplementation may be necessary or beneficial for certain individuals. Understanding when and how to supplement can help ensure optimal B vitamin status while avoiding potential risks.
Supplementation may be particularly appropriate for:
- Older adults: B12 absorption decreases with age due to reduced stomach acid production
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: Requirements increase significantly
- Individuals with gastrointestinal disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or after certain GI surgeries
- Those with alcohol dependency: Alcohol interferes with B vitamin absorption and increases excretion
- Individuals taking certain medications: Including proton pump inhibitors, metformin, and some anticonvulsants
- Those following restrictive diets: Particularly strict vegans (B12) or low-calorie diets
- Individuals with genetic variations: Some people have genetic differences affecting B vitamin metabolism
When supplementing, consider these guidelines:
- Choose B-complex formulations: Since B vitamins work synergistically, a balanced B-complex supplement is often preferable to single B vitamin supplements (except in specific medical situations)
- Look for bioavailable forms: Methylcobalamin (B12), methylfolate (folate), and pyridoxal-5-phosphate (B6) are often better utilized than their synthetic counterparts
- Consider timing: B vitamins can be energizing, so morning consumption is often recommended
- Be aware of dosage: More isn’t always better. Follow recommended dosages unless directed otherwise by a healthcare provider
Regarding potential interactions, be cautious if taking:
- Antibiotics (tetracyclines, quinolones)
- Anti-seizure medications
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Diuretics
Signs that might indicate B vitamin deficiency include unusual fatigue, skin issues, cracks at mouth corners, tongue inflammation, irritability, depression, numbness or tingling in extremities, anemia, and cognitive changes.
While B vitamins are water-soluble and excess is typically excreted in urine, some can cause adverse effects at very high doses. Niacin can cause flushing; B6 can cause nerve damage at sustained high doses; and excessive folate may mask B12 deficiency signs.
Before beginning any supplementation regimen, consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended, especially for individuals with existing health conditions or those taking medications.
Conclusion
The comprehensive health benefits of vitamin B complex underscore its fundamental importance to virtually every system in the human body. From providing the cellular energy that powers physical movement to supporting the complex brain functions that define our cognitive experience, B vitamins truly serve as essential micronutrients for optimal health.
The synergistic nature of these eight vitamins highlights the importance of ensuring adequate intake of the complete B complex rather than focusing exclusively on individual B vitamins. While each has specific functions, their collaborative metabolic relationships mean they function best when present in balanced proportions.
For most individuals, a varied diet rich in whole foods provides the foundation for adequate B vitamin intake. Nutrient-dense foods like whole grains, quality protein sources, legumes, leafy greens, and a variety of fruits and vegetables supply B vitamins in their most natural and bioavailable forms.
However, certain life stages, health conditions, genetic factors, and dietary patterns may increase requirements or impair absorption, making supplementation appropriate in specific circumstances. When supplements are necessary, choosing well-formulated products and following evidence-based dosage recommendations helps maximize benefits while minimizing potential risks.
The research supporting B vitamins’ roles in energy production, cognitive health, cardiovascular support, and cellular function continues to expand, reinforcing these nutrients’ status as essential components of any comprehensive approach to health optimization and disease prevention.
By understanding both the individual and collective functions of the B complex vitamins, you can make informed decisions about your nutritional intake—ensuring these crucial nutrients provide their full spectrum of benefits for your immediate wellbeing and long-term health.

